 A Sports Hernia injury can be frustrating for both athletes and doctors. Also known as Athletic Pubalgia, sports hernias are injuries to the core muscles, groin and abdominal region that are important for stability during athletic movements. A sports hernia injury can be extremely painful with activity and a full recovery often requires medical intervention. There are several non-surgical treatment options for sports hernia recovery and chiropractic therapy can help.
A Sports Hernia injury can be frustrating for both athletes and doctors. Also known as Athletic Pubalgia, sports hernias are injuries to the core muscles, groin and abdominal region that are important for stability during athletic movements. A sports hernia injury can be extremely painful with activity and a full recovery often requires medical intervention. There are several non-surgical treatment options for sports hernia recovery and chiropractic therapy can help.
Sports hernias are not your typical hernias. With a traditional hernia, there is protrusion of internal organs or soft tissue through a weak area of the surrounding muscles and connective tissue. Sometimes, the protrusion can be visible and palpable during a physical exam. With a sports hernia, there are no visible or palpable bulges but there are torn muscles or torn connective tissues causing groin pain. Sports hernias are often intially diagnosed as a groin muscle strain. The common muscles injured with athletic pubalgia and sports hernia are the lower abdominal muscles and adductor muscles of the leg. The physician can confirm a torn groin muscle or torn abdominal muscle with specific orthopedic tests and muscle tests during the physical exam. If you have a history of back pain or hip pain, it may also lead to core weakness and a sports hernia.
How Do Sports Hernias And Athletic Pubalgia Develop?
Sports hernias are generally caused by high velocity, high force activities such as twisting, cutting movements and kicking. Common sports include soccer, football and hockey. We also see people with sports hernias who got the injury from basketball, martial arts and ultimate. When the muscles responsible for controlling the pelvis and torso, also known as the “core muscles” or "core stabilizers", are unable to resist high shearing forces, a sports hernia injury can occur suddenly or develop over time due to overuse. Overuse injuries can result from repetitive athletic movements, repetitive occupational demands, poor posture, or unresolved past injuries. Chronic physical stress cause your body to produce tough, dense, scar tissue "adhesions" that alters normal movement and add stress to adjacent tissues.
Symptoms
Doctors and patients often treat sports hernias as a badly pulled groin muscle. The groin pain is the result of a tearing or overstretch injury to the muscles in front of the hip or the inner thigh. This injury makes it painful or difficult to move the leg and lifting the knee or walking may become difficult. Most groin pain injuries come from overuse of the muscles or from a sudden contraction of the muscles. Injury occurs when the overall muscles are overstretched or contracted. There are several symptoms that differentiate sports hernias from a pulled muscle:
- Severe pain in the groin area or lower abdomen that is localized to one spot when doing a sit up
- Severe pain when bending at the torso, sneezing, coughing, twisting or putting pressure on the injured area
- Persistent pain that goes on continuously for hours or days with little to no relief from over-the-counter pain medications or icing
Diagnosis
The most important diagnostic tool for the assessment of athletic pubalgia is the history and physical examination. The doctor will perform specific orthopedic and muscle tests to identify the injured tissues causing the groin pain. Sports hernia is generally a diagnosis of exclusion. It's important to note that the term “hernia” is misleading since there is no protrusion of the soft tissues in the abdomen. There is no bulge in the injured area like there is with regular hernias. Significant pathologies are first ruled out such as gynecological problems, prostatitis, and inflammatory bowel disease. Other sources of groin pain must be ruled out such as femoral acetabular impingement, hip degenerative joint disease, stress fractures, bursitis and inguinal hernias. Athletic pubalgia is difficult to assess through standard diagnostic imaging tests but specific MRI tests can help visualize the sports hernia injury.
Sports Hernia and Athletic Pubalgia Treatment
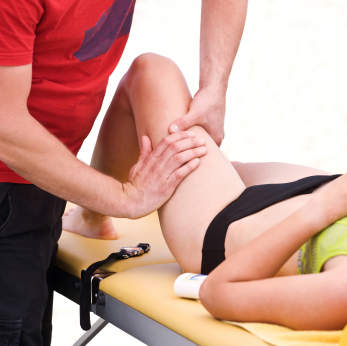
Chiropractic manual therapy should be considered for non surgical treatment of sport hernias. Although some severe cases may still require surgery, many hernias can be treated and managed with conservative manual therapy.
Chiropractic manual therapy will focus on abnormal movement and alignment of the spine, pelvis and hips that delay tissue healing. Treatments typically include:
- Joint manipulation to improve mobility and range of motion
- Active Release Techniques and Graston Technique Soft tissue mobilization to improve muscle flexibility and recovery
- Corrective exercise rehabilitation to control the improved mobility
- Cold laser therapy to decrease inflammation and facilitate tissue healing
If you believe that you have a sports hernia or athletic pubalgia, contact us at 914-42-1502 to schedule a consultation.